The Luna Network HSM 7 is a network device that is intended to be installed in a data center and accessed remotely over a network. Network access to the Luna Network HSM 7 is provided by four 1 Gb/s Ethernet LAN ports. The Luna Network HSM 7 is also equipped with an RJ-45 serial port, used to provide serial access to the appliance for initial network configuration.
NOTE Always employ network security best practices. Place the Luna Network HSM 7 behind a firewall.
The network device interfaces (eth0, eth1, eth2, and eth3) and serial port are located on the rear of the appliance, as illustrated below:
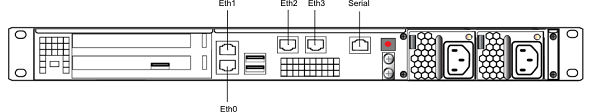
Serial port
Thales recommends using a device connected to the Luna Network HSM 7 appliance serial port to make any changes to the network configuration and routes. If you use an SSH connection to make such changes, the connection can be disrupted by the changes, and associated commands may be interrupted. Partially-configured network settings can make the Luna Network HSM 7 inaccessible via remote SSH connection.
Ethernet LAN device configuration
Depending on the model you chose at time of purchase, the Luna Network HSM 7 is equipped with:
>4 individually-configurable 1 GB/s auto-sensing Ethernet LAN network devices
>2 10G SFP optical Ethernet network interfaces (mapped to eth0/eth1), and two 1G copper RJ45 network interfaces (mapped to eth2/eth3)
You can configure the following network settings for each device:
> IPv4 or IPv6 address. You can configure the addresses using static or DHCP addressing. If you are using IPv6 addressing, you can also use Stateless Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) to have a SLAAC-enabled router in your network automatically configure an IPv6 address on a device.
>Network gateway. IPv4 devices must use an IPv4 gateway. IPv6 devices must use an IPv6 gateway.
>Network mask. IPv4 devices must use dotted-quad format (for example, 255.255.255.0). IPv6 devices can use full or shorthand syntax.
>Static network route.
>DNS configuration. Although you configure DNS at the device level, the settings you configure for a device are available to all devices on the appliance if the configured device is connected to the network. To ensure DNS access, it is recommended that you configure each device. You can configure the following settings:
•DNS nameservers. You can add up to three DNS nameservers.
•DNS search domains.
These settings apply to static network configurations only. If you are using DHCP, the DNS search domains and DNS nameservers configured on the DHCP server are used.
Network Routing Table
The Luna Network HSM 7 appliance software allows you to configure the routing table to suit your network. With appliance software versions older than 7.7.0, you can configure a default route for each network interface or bonded virtual interface (eth0/eth1/eth2/eth3/bond0/bond1). The default route for the device is defined automatically when using DHCP, or by specifying the -gateway option when configuring a static address.
Using Luna Appliance Software 7.7.0 or newer, the network routing table can have one default route only, bound to one network device or bonded virtual interface. The default route is defined automatically when using DHCP, or by specifying the -gateway option when configuring a static address. The first interface configured is automatically assigned the default route. Once a default route is defined, no additional default routes can be defined without deleting the first default route. You can use network show at any time to see which device has the default route set -- Default Route (eth#) : Yes/No.
The default route is tied to the gateway, so interfaces that do not have the default route have their gateway value automatically dropped -- the Gateway field in the output from network show will be empty.
Use the network route commands to make changes to the routing table.
CAUTION! A change to network routing when updating to Luna Appliance Software 7.7.0 or newer, from any prior 7.x version, can cause your appliance to become unreachable via network connection. Older appliance versions permitted the existence of multiple default routes. Beginning with Luna Appliance Software 7.7.0, only one instance of the default route can exist.
Options for a successful update with minimal disruption are:
>Remove all but one instance of the ‘default route’, using the network route delete command, before upgrading from any appliance software version older than Luna Appliance Software 7.7.0.
>Connect locally via serial cable to perform the update, so your access to the network appliance is not lost when network connection becomes temporarily unavailable (pending proper network configuration).
Note also that if you re-image, going back to a version older than Luna Appliance Software 7.7.0, the routing table goes back to the old format and you must apply one of the above precautions again, to update.
If the above precautions are not taken and the appliance becomes unreachable, complete the following steps to restore connection to the appliance:
1.Connect locally via serial cable.
2.Delete all network interfaces. See network interface delete.
3.Configure a network interface to use a default route by doing one of the following:
•Configure the network interface to use a static IP configuration while specifying the -gateway option. See network interface static.
•Configure the network interface to use DHCP. See network interface dhcp.
After you complete the above steps, network connectivity to the appliance is restored and any remaining interfaces that are configured do not have a default route set.
The Luna Network HSM 7 supports port bonding. Port bonding allows you to create a bond between two interfaces (eth0 and eth1, or eth2 and eth3) into a single bonded interface (bond0 or bond1). In a bonded interface, both ports are bound to a virtual interface with a single IP address, with one port active and one port standby. See Luna Network HSM 7 Appliance Port Bonding for more information.
NTLS Binding
You can bind the NTLS traffic (used to securely transport cryptographic messages exchanged between a client and the HSM across the network) to a specific Ethernet device (eth0, eth1, eth2, eth3, bond0, bond1, all) on the appliance. This allows you to divide the traffic going to the appliance into cryptographic (destined for the HSM) and administrative (LunaSH) streams, for enhanced security and performance. See Binding Your NTLS or SSH Traffic to a Device for more information.
SSH Binding
You can optionally bind/restrict the SSH traffic (used to securely transport administrative messages across the network) to a specific Ethernet device (eth0, eth1, eth2, eth3, bond0, bond1, all) on the appliance, to the appliance hostname, or to a specific IP address. This allows you to divide the traffic going to the appliance into cryptographic (destined for the HSM) and administrative (LunaSH) streams, for enhanced security and performance. By default, SSH traffic is unrestricted. See Binding Your NTLS or SSH Traffic to a Device for more information.
Gathering Appliance Network Information
Before you begin, obtain the following information (see your network administrator for most of these items):
HSM Appliance Network Parameters
>IP address and subnet mask for each LAN port you want to use (if you are using static IP addressing)
>Hostname for the HSM appliance (registered with network DNS)
>Domain name (per port)
>Default gateway IP address (per port)
>DNS Name Server IP address(es) (per port)
>Search Domain name(s) (per port)
>Device subnet mask (per port)
DNS Entries
>Ensure that you have configured your DNS Server(s) with the correct entries for the appliance and the client. The HSM appliance expects fully qualified hostnames.
>If you are using DHCP, then all references to the Client and the HSM appliance (as in Certificates) should use hostnames.
Other Considerations
Clients need to be able to route directly to each HSM appliance they need to talk to, with no load balancing in place. The Luna Network HSM 7 does not work with off-the-shelf load balancers and service discovery techniques. You can NAT or forward the traffic so long as it always goes to the same place so the TLS tunnel isn’t terminated by outside forces.
Some Network Configuration Best Practices
Consider how you would proceed for (say) a Linux server with very sensitive data and that contains 4 NICs. Whatever you would do for the most sensitive servers you have, that’s what you should do for the HSMs.
Do you separate flows between admin networks and application network? Then do that with the HSM.
Do you divide into 3 layers like DMZ/L1/L2 and put sensitive equipment in the L2 network? Then do that with the HSM.
Do you put the sensitive servers behind a firewall or particular router? Then do that with the HSM.
Do you set specific routes in your Linux servers? Then do that with the HSM.
Do you use specific DNS servers with internal split views? Then do that with the HSM, for the same reasons.
Configuring the Network Parameters
You can use the serial connection to configure all of your network parameters now, or you can perform a minimal configuration now, where you only configure a single port, and then use the configured port to access the appliance over the network and complete the configuration.
NOTE Use a locally connected serial terminal when changing the appliance IP address, to avoid SSH admin console disconnection due to the change.
To configure the appliance and port network parameters
You can configure all of the ports now, using the serial connection, or you can configure only one port now, and then use a network connection to that port to configure the remaining ports. It is recommended that you configure and test each device. You need to know the IP address of at least one network interface to establish a SSH connection to the appliance.
Once configured, you can find the interface IP addresses on the appliance's front-panel LCD screen. If there is no IP address shown on the LCD, you must use a serial port connection to connect to the appliance.
1.Configure the IP address, network mask, and gateway (optional) on at least one of the Ethernet LAN ports, using the network interface commands. You can configure the ports to use an IPv4 or IPv6 address. A mix of IPv4 and IPv6 ports is supported. If you are configuring the device using DHCP, the first device configured will receive the default route for the appliance. If you are configuring a static address, the -gateway option is used to define the default route. The first device configured with a gateway receives the default route.
CAUTION! Clients connecting to the appliance must use the same IP version that is configured on the port they are connecting to, so that certificates resolve. That is, all clients connecting to an IPv4 port must have an IPv4 address, and all clients connecting to an IPv6 port must have an IPv6 address.
•If you are configuring an IPv4 address, you can configure a static address, or use DHCP.
| Static | lunash:> network interface static -device <netdevice> -ip <IP_address> -netmask <netmask> [-gateway <IP_address>] |
| DHCP | lunash:> network interface dhcp -device <netdevice> |
•If you are configuring an IPv6 address, you can configure a static address, configure the port to obtain an IPv6 address using the Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) protocol, or use DHCP. To use SLAAC, you must have a SLAAC-enabled router in your network.
| Static | lunash:> network interface static -device <netdevice> -ip <IP_address> -netmask <netmask> [-gateway <IP_address>] -ipv6 |
| SLAAC | lunash:> network interface slaac -device <netdevice> |
| DHCP | lunash:> network interface static -device <netdevice> -ipv6 |
You are prompted to confirm the action. If no network cable is attached to the port you configured, the following message is displayed:
Warning. Unable to activate interface <netdevice> Ensure that the network cable is connected.
This message is informational. The interface will automatically activate when you connect a network cable to the port.
2.[Optional] If you wish to use the Port Bonding feature described above to configure bond0 and/or bond1 interface, you can configure it now. If one of the secondary interfaces within the bond has the default route, the bonded interface receives the default route.
CAUTION! Using Luna Appliance Software 7.8.3 or older, once the default route is added to the bonded interface, disabling the bond for any reason will cause a loss of SSH connectivity to the Luna Network HSM 7. It is highly recommended that you configure manual routes on at least one of the secondary interfaces within the bonded interface (eth0 or eth1 for bond0, eth2 or eth3 for bond1). Refer to Disabling a Bonded Interface.
lunash:> network interface bonding config
lunash:> network interface bonding enable
See Luna Network HSM 7 Appliance Port Bonding for more information.
3.[Optional] Make any desired changes to the appliance network routing table.
Using older versions of the Luna Appliance Software, each network device can be configured with its own default route. Using Luna Appliance Software 7.3.3, Luna Appliance Software 7.4.2, or Luna Appliance Software 7.7.0 and newer, only one default route may be configured on the appliance. The first network route configured (either automatically using DHCP, or by specifying a valid -gateway option when configuring a static IP on a network device) becomes the default route. If you wish to change this default route, you must first delete the original default route. This applies if the default route has been applied on a network interface and you want to enable it on a different interface. The default route remains constant if you switch the device between static and DHCP address selection. See Network Routing Table for more information, and refer to the following example procedures:
To move the default route from eth0 to eth1
a.[Optional] Display the current network settings.
lunash:> network route show
b.Remove the default route from eth0. When the default route is removed from a network device or bonding interface, the gateway is automatically dropped.
lunash:> network route delete network <IP_address> -device eth0 -gateway 0.0.0.0
c.Add the default route to eth1. This step is different depending on your appliance software version:
–Using one of the appliance software versions mentioned above (7.3.3, 7.4.2, 7.7.x), add the network route to an already-configured eth1.
lunash:> network route add network <IP_address> -device eth1 -gateway 0.0.0.0
–Using Luna Appliance Software 7.8.0 or newer, reconfigure eth1.
lunash:> network interface static -device eth1 -ip <ip address> -netmask <netmask> -gateway <gateway>
Now you can add manual network or host routes as required for your desired network flow.
4.[Optional] Set the appliance hostname and domain name. You can specify a simple hostname or a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) using the format <hostname.domainname>. If you supply a hostname that includes a space, all text after the space is ignored. For example, if you typed network hostname my hsm the system would assign a hostname of “my”. Therefore, if you want "my hsm", use "my_hsm", "my-hsm", or similar.
lunash:> network hostname <hostname>
NOTE This command replaces the network domain command from Luna 5/6.
You must configure your DNS server to resolve the hostname to the IP address configured on the Ethernet port of the appliance. Do this for each Ethernet port you are configuring. See your network administrator for assistance.
5.[Optional] If you wish to use the NTLS or SSH binding features described above to restrict NTLS or SSH messages to an interface (eth0, eth1, eth2, eth3, bond0, bond1, all), use the ntls bind or sysconf ssh commands. See Binding Your NTLS or SSH Traffic to a Device for more information.
6.[Optional] Add a domain name server to the network configuration for the appliance. The name server is added to the appliance DNS table. You can add up to three different DNS name servers to the appliance DNS table. There is one DNS table that applies to all network devices (ports) on the appliance.
NOTE The domain name settings apply to static network configurations only. If you are using DHCP, the DNS name servers configured on the DHCP server are used.
When you add a DNS server, you add it to a specific network device on the appliance (eth0, eth1, eth2, eth3, bond0, bond1). When you add a DNS server to a device, it is added to the DNS table for the appliance and becomes available to all devices on the appliance, provided the device you added it to is connected to the network. For example, if you add a DNS server to eth0, all devices will be able to access the DNS server if eth0 is connected to the network. If eth0 is disconnected from the network, access to the DNS server is lost for any devices to which you did not add the DNS server. To ensure that any DNS server you add is available in the event of a network or port failure, it is recommended that you add it to all devices you will use to connect the appliance to the network.
lunash:> network dns add nameserver <ip_address> -device <net_device>
NOTE You must restart the ntls service (lunash:> service restart ntls) for DNS changes to take effect.
7.[Optional] Add a search domain to the network configuration for the appliance. Search domains allow you to avoid typing the complete address of frequently used Internet domains by automatically appending the search domain to an internet address you specify in LunaSH. For example, if you add the search domain mycompany.com, entering the command network ping hsm1 would search for the domain hsm1.mycompany.com. If the domain resolves, it would ping the device with that hostname.
The search domain is added to the appliance DNS table. You can add a maximum of six search domains totaling no more than 256 characters.
NOTE The search domain settings apply to static network configurations only. If you are using DHCP, the DNS search domains configured on the DHCP server are used.
When you add a DNS search domain, you add it to a specific network device on the appliance (eth0, eth1, eth2, eth3, bond0, bond1). When you add a search domain to a device, it is added to the DNS table for the appliance and becomes available to all devices on the appliance, provided the device you added it to is connected to the network. For example, if you add a search domain to eth0, all devices will use the search domain if eth0 is connected to the network. If eth0 is disconnected from the network, the search domain is not used by any devices to which you did not add the search domain. To ensure that any search domain you add is available in the event of a network or port failure, it is recommended that you add it to all devices you will use to connect the appliance to the network.
lunash:> network dns add searchdomain <domain> -device <net_device>
NOTE You must restart the ntls service (lunash:> service restart ntls) for DNS changes to take effect.
If you have chosen to perform setup via SSH, rather than via the direct (serial) administrative connection, then you will likely lose your network connection at this point, as you confirm the change of IP address from the default setting.
8.Display the current network settings, so you can verify that they are now correct for your environment before attempting to use them.
lunash:> network show
