JWT-Secured Authorization Request
You can configure a web client to use a JWT-Secured Authorization Request (JAR). JAR is an OpenID Connect and OAuth 2.0 security mechanism that protects authorization requests by moving request parameters into a signed JSON Web Token (JWT). JAR is standardized in RFC 9101.
In a standard authorization request, parameters such as redirect_uri, scope, and code_challenge are sent as plain query parameters. Although HTTPS protects the transport, these parameters are not cryptographically bound to the client.
JAR addresses common authorization-request threats:
- Parameter tampering: Attackers attempt to change request parameters (for example,
redirect_uriorscope). - Request injection: Attackers attempt to inject additional parameters or override existing ones.
- Lack of authenticity: The authorization server cannot prove that the request parameters were created by the client (beyond the presence of
client_id).
With JAR, the client creates a request object (a JWT), signs it with its private key, and sends it in the authorization request using the request parameter. The authorization server validates the JWT signature and then processes the contained authorization request claims.
Supported mechanism
The OneWelcome Identity Platform implements JAR by value using only the request parameter.
- ✅ Use:
request=<signed-jwt> - ❌ Not supported:
request_uri=<url>
Benefits of JAR
-
Enhanced security:
- Integrity protection: Any modification of request parameters is detected by signature verification.
- Authenticity verification: The authorization server can verify that the request parameters were created by the client that holds the private key.
-
Compliance and assurance:
- Stronger assurance for high-risk applications: Helps meet requirements where critical request parameters must be integrity-protected.
- Better auditability: The exact request can be logged (or stored) and validated later.
How JAR works
Standard authorization request (without JAR)
In a standard OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect authorization request, parameters are sent in the query string:
GET /oauth/v1/authorize?
response_type=code&
client_id=web-client-123&
redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fclient.example.com%2Fcallback&
scope=openid%20profile&
state=af0ifjsldkj&
code_challenge=E9Melhoa2OwvFrEMTJguCHaoeK1t8URWbuGJSstw-cM&
code_challenge_method=S256 HTTP/1.1
Host: tokenserver.example.com
Authorization request with JAR
With JAR, the client places the authorization request parameters in a signed JWT (the request object) and sends it using the request parameter:
GET /oauth/v1/authorize?
client_id=web-client-123&
request=eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IjIwMjUtMDEtMDEiLCJ0eXAiOiJKV1QifQ.eyJjbGllbnRfaWQiOiJ3ZWItY2xpZW50LTEyMyIsInJlc3BvbnNlX3R5cGUiOiJjb2RlIiwicmVkaXJlY3RfdXJpIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9jbGllbnQuZXhhbXBsZS5jb20vY2FsbGJhY2siLCJzY29wZSI6Im9wZW5pZCBwcm9maWxlIiwic3RhdGUiOiJhZjBpZmpzbGRraiIsImNvZGVfY2hhbGxlbmdlIjoiRTlNZWxob2EyT3d2RnJFTVRKZ3VDSGFvZUsxdDhVUldidUdKU3N0dy1jTSIsImNvZGVfY2hhbGxlbmdlX21ldGhvZCI6IlMyNTYiLCJleHAiOjE3MzU2ODAwMDAsImlhdCI6MTczNTY3OTcwMH0.signature HTTP/1.1
Host: tokenserver.example.com
The authorization server verifies the signature, validates the JWT claims (including timestamps), and then treats the payload claims as the authorization request parameters.
Request object structure
A JAR request object is a JWT consisting of the following high-level structure:
- Header: Algorithm and key identifier (for example,
alg,kid,typ) - Payload: Authorization request parameters as claims (for example,
client_id,response_type,redirect_uri,scope,state,code_challenge, and so on) - Signature: Created with the client’s private key
Authorization flow with JAR
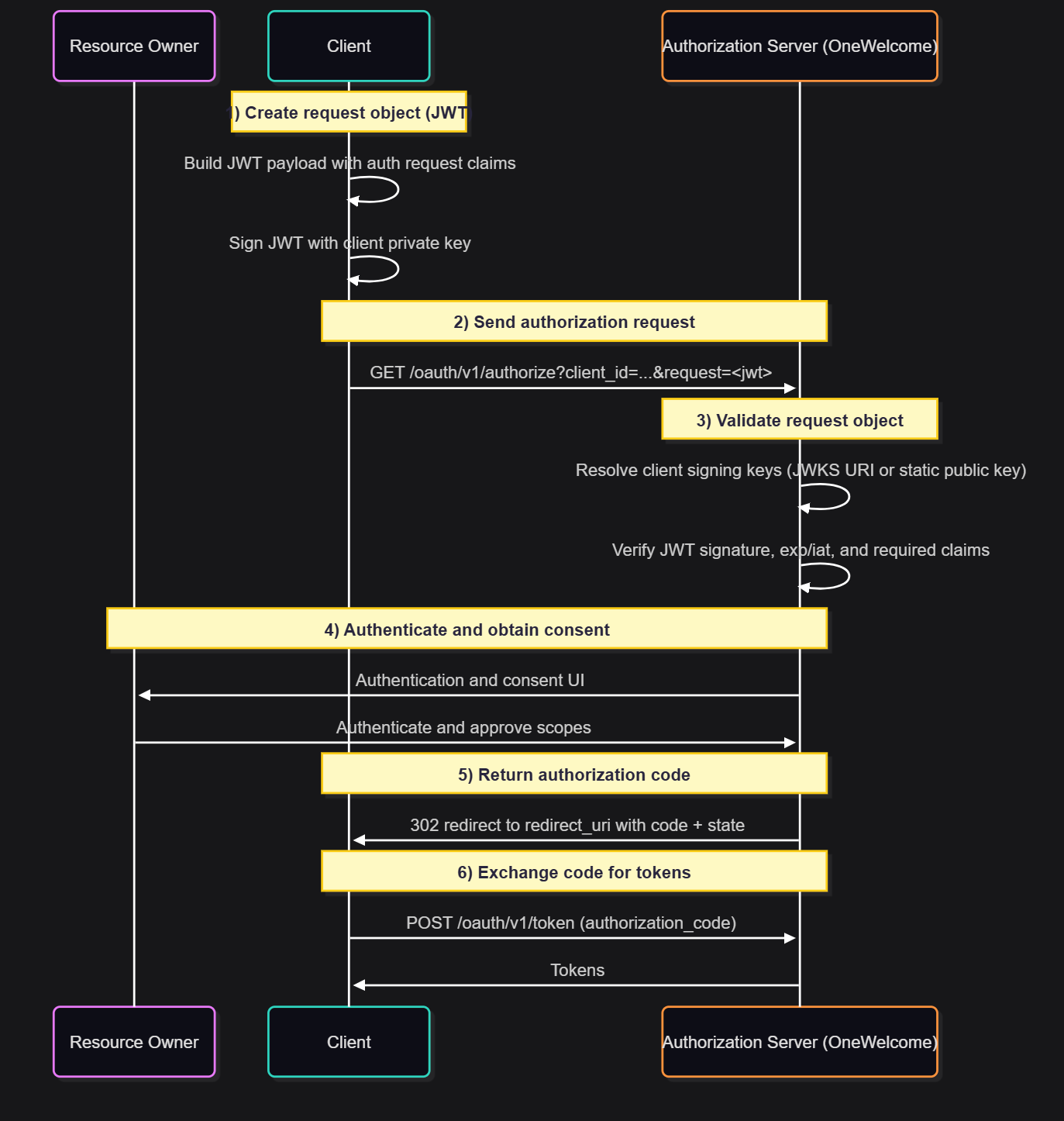
Flow details
- Client creates the request object: The client builds a JWT payload containing the authorization request parameters.
- Client signs the request object: The JWT is signed using the private key associated with the client.
- Client sends the authorization request: The signed JWT is sent as the
requestparameter. - Authorization server validates the JWT: Signature verification and claim validation is performed before processing the request.
- User authenticates and grants consent: Normal OIDC user interaction occurs.
- Authorization code flow continues: The client exchanges the code for tokens.
JWT structure
JWT header
The header includes the algorithm and key identifier (for example, alg, kid, typ).
Typical header fields
{
"alg": "RS256",
"kid": "2025-01-01",
"typ": "JWT"
}
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
alg |
yes | Signature algorithm used to sign the request object |
kid |
recommended | Key identifier, used by the authorization server to select the correct public key |
typ |
recommended | Token type: Use JWT |
JWT payload
The payload contains standard OAuth 2.0 or OIDC authorization request parameters as JWT claims.
Common claims
| Claim | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
client_id |
yes | Client identifier: Must match the client_id request parameter |
response_type |
yes | Typically code |
redirect_uri |
yes | Redirect URI: Must match a configured redirect URI for the client |
scope |
yes | Requested scopes (space-separated string) |
state |
recommended | CSRF protection: Returned to the client in the authorization response |
nonce |
depends | Recommended for OpenID Connect flows when an ID token is returned |
code_challenge |
depends | PKCE code challenge: Required for public clients using authorization code flow |
code_challenge_method |
depends | PKCE method: Typically S256 |
prompt |
no | OIDC prompt values |
login_hint |
no | Hint for user identification |
acr_values |
no | Requested ACR values |
ui_locales |
no | Preferred UI locales |
max_age |
no | Maximum authentication age |
JWT timestamp or validation claims
| Claim | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
exp |
no | Expiration time: If provided, must be in the future at validation time |
iat |
no | Issued-at time |
nbf |
no | Not-before time |
iss |
no | If provided it should contain the client_id |
aud |
yes | Should contain the auth server identifier |
What the authorization server validates
When JAR is used, the OneWelcome Identity Platform validates the following, at minimum:
- JWT signature using the configured client public key (dynamic JWKS URI or static public key)
- Expiration (
exp) - Required OAuth parameters in the payload (
client_id,response_type,redirect_uri, and so on) - Redirect URI is registered for the client
If present, the following are also validated:
- Issuer (
iss) - Audience (
aud)
Signature algorithms
The following signature algorithms are supported for request object signing:
- RSA:
RS256,RS384,RS512 - Elliptic Curve:
ES256,ES384,ES512
API discovery
JAR support is advertised via the OpenID Provider discovery document, which you can access via the Discovery API.
Configure a web client to use JAR
This section explains how to configure a web client to use JAR.
Prerequisites
Before you enable JAR, ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
- You have a web client configured for the authorization code grant.
- The client can create and sign JWTs.
-
You have a signing key pair available for the client:
- EC: minimum P-256
- RSA: minimum 2048 bits, maximum 4096 bits
-
The public key is available to the OneWelcome Identity Platform either:
- dynamically via a JWKS URI, or
- as a static public key (plain public key).
Add JAR to a web client
To use JAR, the Grant type must be Authorization code.
-
On the Access Admin console, go to Configuration > Web Clients.
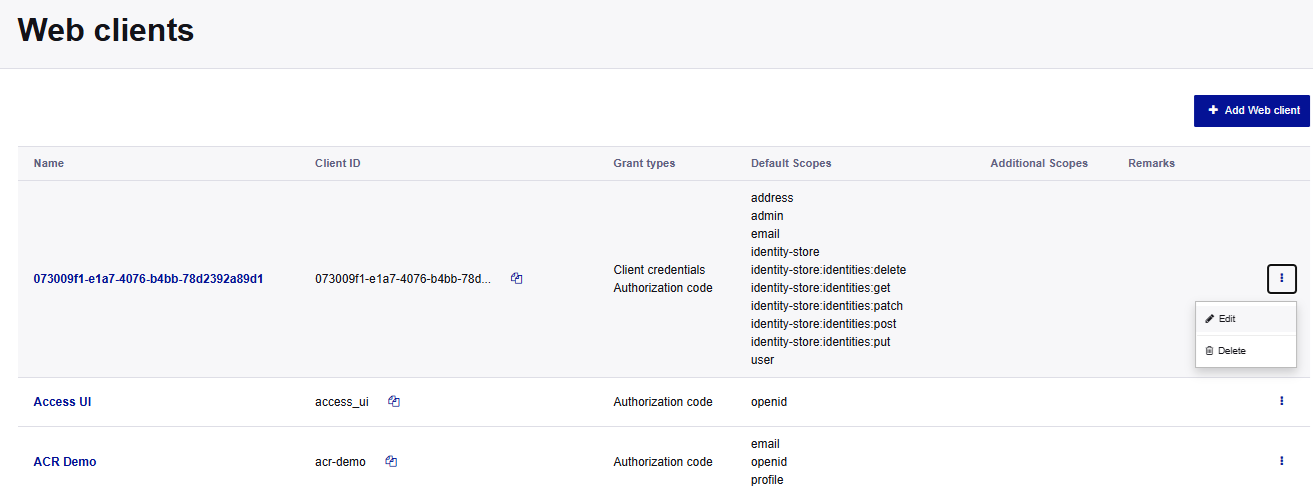
-
In the menu for your web client, select Edit or select Add Web client.
-
On the Edit Web client or Add Web client page, under OAuth settings, ensure that the Grant types is Authorization code.
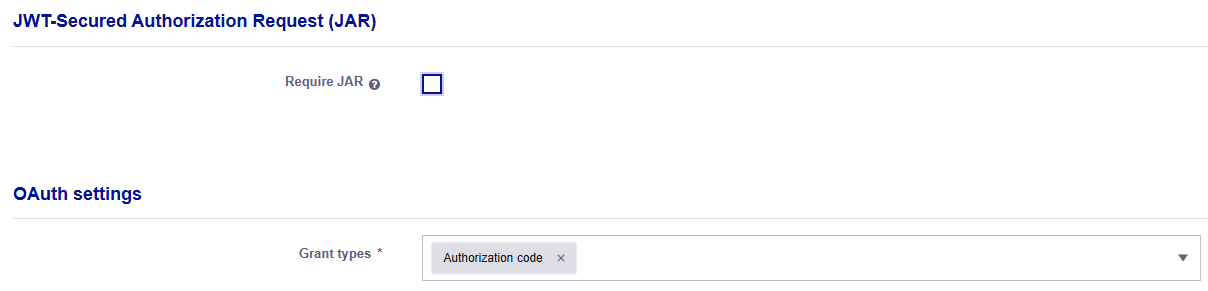
-
In the JWT-Secured Authorization Request (JAR) section, select the Require JAR check box.
Require JAR is mandatory
When the Require JAR is selected for a web client, every authorization request for that client must include a valid signed request object in the
requestparameter. Requests withoutrequest(or with an invalid request object) are rejected.When you select the check box, the JWT Signing Configuration options are added to the web client.
Configure JWT signing
JAR uses the same client key configuration as private key JWT client authentication.
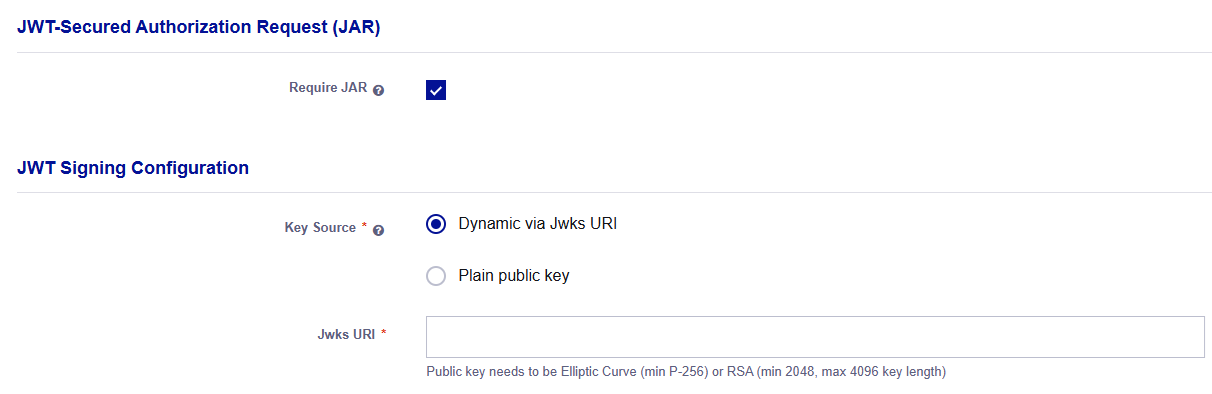
-
On the Edit Web client or Add Web client page, under JWT Signing Configuration, select the Key Source:
-
Dynamic via Jwks URI: Provide a JWKS URI with public keys for private key JWT authentication.
-
Plain public key: (Static JWT Configuration) Upload a Plain public key for private key JWT authentication.
The public key must meet these requirements:
- Elliptic Curve (EC): minimum P-256
- RSA: minimum 2048 bits, maximum 4096 bits
-
Configure encrypted request objects
In addition to signing JSON Web Signature (JWS), request objects can be encrypted using JSON Web Encryption (JWE) at the system level, to hide authorization request parameters from the user agent and intermediaries.
For more information about encrypting request objects, see OpenID provider configuration.
-
On the Access Admin console, configure encrypted request objects under System > JWT Key Configuration > Token Encryption.
Limitations
- By-value only: Only the
requestparameter is supported. Therequest_uriis not implemented. - Client configuration controls enforcement:
- If Require JAR is enabled, JAR is mandatory.
- If it’s not enabled, JAR is optional and standard requests are accepted.
- Supported signing algorithms:
RS256,RS384,RS512,ES256,ES384,ES512. - Performance: JWT signing and verification add CPU overhead, especially at high authorization request rates.
- Token size: Request objects can be significantly larger than query parameters. Keep request objects small to avoid URL length limits in browsers or proxies.

