Risk management
In today’s environment, with everything increasingly online, organizations face mounting challenges, from regulatory changes to cyber threats where risks are not only financial but also reputational. Proactive risk management is essential for maintaining business continuity, meeting compliance obligations, and protecting critical assets.
OneWelcome Identity Platform Risk Management is a cloud-based solution that helps enterprises identify, assess, monitor, and mitigate risks across digital channels. It is grounded in financial-services–grade controls and analytics, meeting the high bar set by banks and insurers, while supporting organizations with stringent risk and compliance obligations through consistent, policy-driven protection.
Risk management services are at the heart of our OneWelcome Identity Platform, to secure and enhance onboarding and access to digital services. They allow organizations to assess every single online session in real time and seamlessly (without user interaction), to evaluate the risk and select the most appropriate actions.
-
During the onboarding process, risk management can be used to provide identity affirmation, that is, the possibility to complement the identity proofing process by providing assurance for a claimed identity.
-
For access to digital services, risk management can determine the most appropriate authentication method to use: allow the operation, block it, or challenge the user with step-up authentication, all running silently in the background to provide the best user experience.
Risk management editions
-
Essential: Provides fundamental rules for making decisions about login flows on desktop and mobile web, delivered via OneWelcome Identity Platform-hosted pages.
-
Enhanced: Provides an advanced risk-based engine with policies, risk scores, and comprehensive rule sets to tackle complex fraud (such as phishing or social engineering) using an ML model. The use cases cover any type of sensitive actions from account creation to transfer, login, new beneficiary, and so on. Integration is done via restful API, JavaScript for web, and mobile-native SDKs.
Essential edition documentation
Use in login flows
Risk management can be used in login flows to branch the user journey based on the evaluated risk level (low, medium, high) and apply step-up authentication when needed.
How it works
-
Signal collection: Device and context signals are captured from user devices via a lightweight JavaScript snippet (web) and mobile SDKs (Android/iOS).
-
Real-time, on-demand evaluation: Risk is categorized as Low, Medium, or High per event in real time, enabling immediate decisions.
-
Actionable outcomes: Policy-driven decisions that Allow, Deny, or Challenge (such as step-up authentication), minimize friction for trusted users while increasing protection.
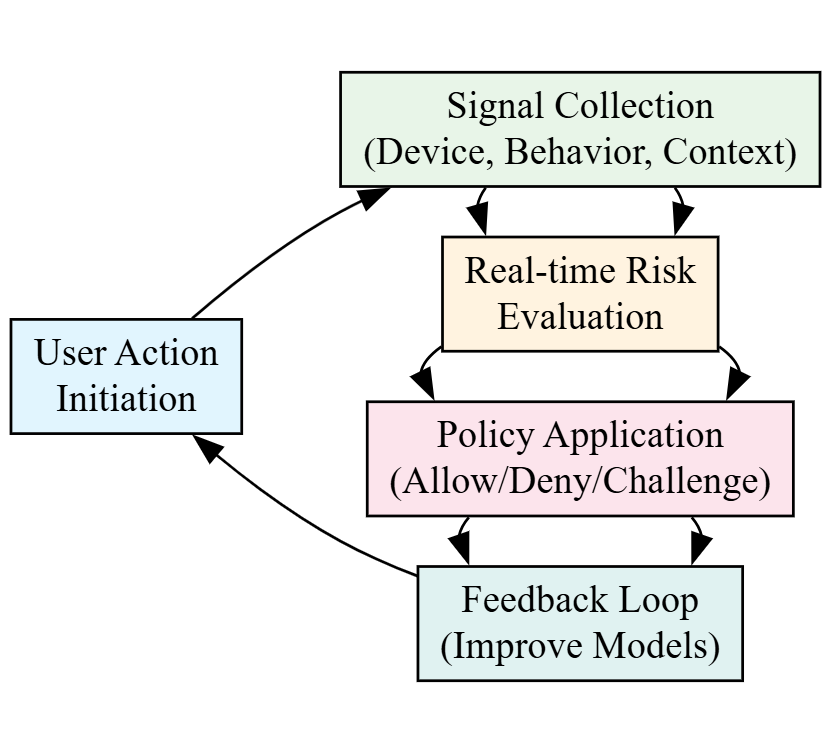
Following each risk evaluation, the service leverages outcome feedback, whether an action was allowed, challenged, or denied, and uses it to refine future risk decisions. Positive signals (such as a recent successful authentication on a recognized device) lower friction for trusted, recurring users, while confirmed fraud reports strengthen detection—improving accuracy and reduce false positives for a better user experience. Depending on the implementation, feedback collection can be automatic or require additional integration.
What is a policy?
A policy defines the decision logic for a risk evaluation. It considers context signals, rules, and scores to determine an outcome: allow, challenge, or deny.
How a policy works
-
A policy contains ordered scenarios (conditions based on context, rules, and scores).
-
Scenarios are evaluated from top to bottom.
-
The first matching scenario returns its associated decision.
-
If no scenario matches, the policy either returns its default decision or passes control to the next policy.
Multiple policies
-
You can define multiple policies, which are evaluated in the order that they are listed.
-
A policy is only evaluated if its operating context matches the request’s scope, otherwise it is skipped.
-
Evaluation continues until a decision is made or the default policy is reached.
Scope and operating context
-
When requesting a risk evaluation, you do not specify a policy directly.
-
You provide a scope (such as a use case, user or transaction type, or environment).
-
A policy is considered only if its operating context matches that scope.
Scenarios or steps
-
A policy can contain zero or more scenarios.
-
Scenarios are evaluated in the order that they are listed.
-
Each scenario has an associated decision and is defined with one or more conditions.
-
A scenario matches only if all of its conditions are met.
-
When a scenario matches, evaluation stops. No further scenarios or policies are evaluated, and the scenario’s decision is returned.

