Secured resource access
Resource calls made with the Onegini SDK are always secured with certificate pinning. Payload encryption can be enabled in the Token Server. Debug detection can be configured in the Config Model, if enabled the SDK will verify there is no debugger attached to the app process before fetching the resource. SDK does not perform any mapping or conversion of the response payload. It is up to the App how to process a valid response from the back-end.
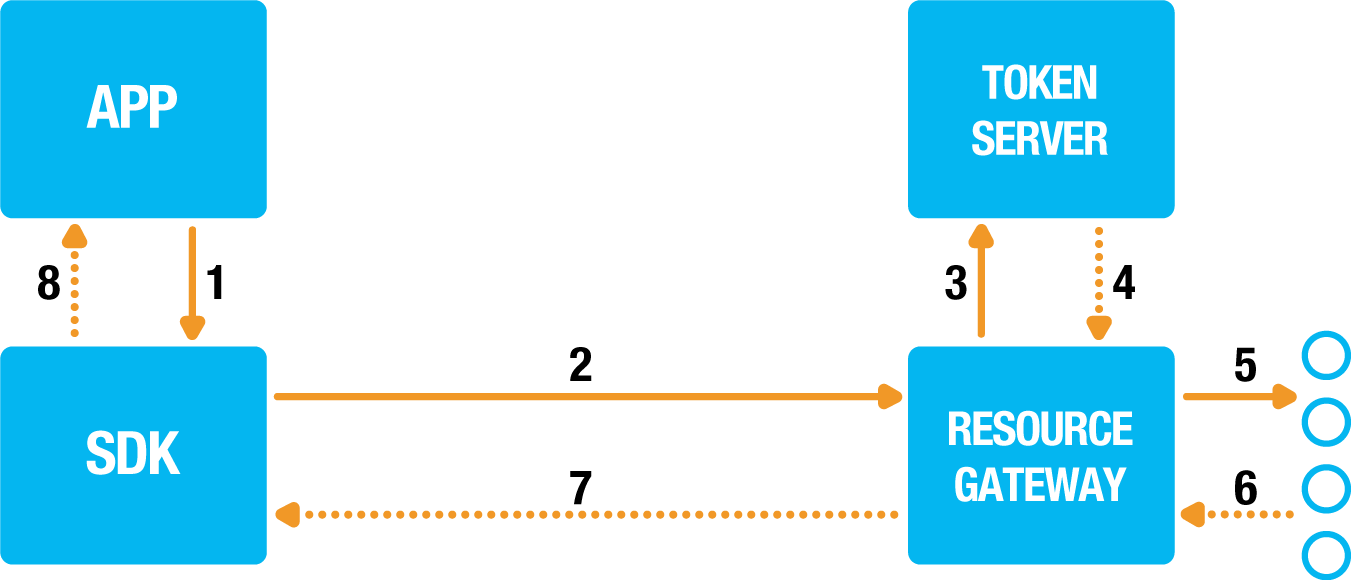
Get resource flow:
1. APP -> SDK: Instruct the SDK to request a resource.
2. SDK -> Resource Gateway: Request a resource at the resource gateway by sending the access token in the request.
3. Resource Gateway -> Token Server: Validate the provided token.
4. Token Server --> Resource Gateway: Details regarding the access token like scope and user, which will be verified by the resource gateway.
5. Resource Gateway -> Resource Server: Get the resource.
6. Resource Server --> Resource Gateway: Return the resource.
7. Resource Gateway --> SDK: Return the resource.
8. SDK --> APP: Resource is returned to the APP which has knowledge of the context of the returned resource.
The SDK can fetch a secure resource in three distinct ways. For a resource that is tied to a user (e.g. account information or transactions), the SDK can execute an Secured resource access. For a resource that is tied to an application but are not unique per user, for example application assets, the SDK can execute an Anonymous request. For a resource that can be fetched without any additional authentication, but for which you would still like to use certificate pinning and jailbreak/debug detection the SDK can execute an Unauthenticated requests.
Authenticated requests
Secure resource access is performed using UserClient for authorized calls and DeviceClientfor anonymous calls.
Instances can be obtained by using userClient and deviceClient respectively, or by calling SharedUserClient.instanceand SharedDeviceClient.instance` respectively. Attempt to obtain clients instances without configuring the SDK first, will result in throwingNSInternalInconsistencyException` exception.
Performing a resource call
For user specific resources the user needs to be authenticated and a token that is connected to the authenticated user is presented to the back-end when fetching a resource.
The SDK requires that the user is authenticated. Fetching user specific resources using the Onegini SDK is done through the following UserClient method:
@discardableResult
func sendAuthenticatedRequest(_ resourceRequest: ResourceRequest,
completion: @escaping ((ResourceResponse?, Error?) -> Void))
-> NetworkTask?
- (nullable ONGNetworkTask *)fetchResource:(ONGResourceRequest *)request completion:(nullable void (^)(ONGResourceResponse * _Nullable response, NSError * _Nullable error))completion;
Example of an authenticated resource call
let request = ONGResourceRequest(path:"_api_users_" method:"GET")
ONGUserClient.sharedInstance().fetchResource(request) { response, error in
__ handle response
}
ONGResourceRequest *request = [[ONGResourceRequest alloc] initWithPath:@"_api_users" method:@"GET"];
[[ONGUserClient sharedInstance] fetchResource:request completion:^(ONGResourceResponse * _Nullable response, NSError * _Nullable error) {
__ handle response
}];
Implicit requests
Implicit resource requests are performed using the UserClient. It can be obtained by using the
userClient of the Client object or by calling the SharedUserClient.instance method.
Performing a resource call
Implicit resource calls are authenticated using an implicit access token. It is obtained by the SDK during implicit user authentication. You can find more information about the process in the Implicit user authentication guide. Fetching implicit resources using the Onegini SDK is done through the following ONGUserClient method:
@discardableResult
func sendImplicitRequest(_ resourceRequest: ResourceRequest,
completion: @escaping ((ResourceResponse?, Error?) -> Void))
-> NetworkTask?
- (nullable ONGNetworkTask *)fetchImplicitResource:(ONGResourceRequest *)request completion:(nullable void (^)(ONGResourceResponse *_Nullable response, NSError *_Nullable error))completion;
Example of an implicit resource call
let request = ONGResourceRequest(path:"_api_users_" method:"GET")
ONGUserClient.sharedInstance().fetchImplicitResource(request) { response, error in
__ handle response
}
ONGResourceRequest *request = [[ONGResourceRequest alloc] initWithPath:@"_api_users" method:@"GET"];
[[ONGUserClient sharedInstance] fetchImplicitResource:request completion:^(ONGResourceResponse * _Nullable response, NSError * _Nullable error) {
__ handle response
}];
Anonymous requests
Secure anonymous resource access is performed using the DeviceClient. It can be obtained by using the
deviceClient of the Client object or by calling the SharedDeviceClient.instance method. Any
attempt to obtain the DeviceClient without configuring the SDK first, will result in throwing a NSInternalInconsistencyException exception.
Performing a resource call
For anonymous resources a token that is connected to this device is presented to the back-end. Anonymous resource calls allow you to fetch data that is not user specific but should not be publicly available to anybody knowing the API.
The SDK requires the device (application) to be registered, valid and authenticated. Fetching anonymous resources using the Onegini SDK is done through the
following DeviceClient method:
@discardableResult
func sendAuthenticatedRequest(_ resourceRequest: ResourceRequest,
completion: @escaping ((ResourceResponse?, Error?) -> Void))
-> NetworkTask?
- (nullable ONGNetworkTask *)fetchResource:(ONGResourceRequest *)request completion:(nullable void (^)(ONGResourceResponse * _Nullable response, NSError * _Nullable error))completion;
Example of an anonymous resource call
let request = ONGResourceRequest(path:"_api_users_" method:"GET")
ONGDeviceClient.sharedInstance().fetchResource(request) { response, error in
__ handle response
}
ONGResourceRequest *request = [[ONGResourceRequest alloc] initWithPath:@"_api_users" method:@"GET"];
[[ONGDeviceClient sharedInstance] fetchResource:request completion:^(ONGResourceResponse * _Nullable response, NSError * _Nullable error) {
__ handle response
}];
Unauthenticated requests
Securing unauthenticated requests is performed using the DeviceClient. It can be obtained by using the
deviceClient of the Client object or by calling the SharedDeviceClient.instance method.
attempt to obtain the DeviceClient without configuring the SDK first, will result in throwing a NSInternalInconsistencyException exception.
Performing a resource call
For unauthenticated requests no token is presented to the back end. Only certificate pinning and jailebreak/debug detection are
used when fetching unauthenticated resources. Fetching unauthenticated resources using the Onegini SDK is done through the
following DeviceClient method:
@discardableResult
func sendUnauthenticatedRequest(_ resourceRequest: ResourceRequest,
completion: @escaping ((_ response: ResourceResponse?,
_ error: Error?) -> Void)) -> NetworkTask?
- (nullable ONGNetworkTask *)fetchUnauthenticatedResource:(ONGResourceRequest *)request completion:(nullable void (^)(ONGResourceResponse * _Nullable response, NSError * _Nullable error))completion;
Example of an unauthenticated resource call
let request = ONGResourceRequest(path:"_api_users_" method:"GET")
ONGDeviceClient.sharedInstance().fetchUnauthenticatedResource(request) { response, error in
__ handle response
}
ONGResourceRequest *request = [[ONGResourceRequest alloc] initWithPath:@"_api_users" method:@"GET"];
[[ONGDeviceClient sharedInstance] fetchUnauthenticatedResource:request completion:^(ONGResourceResponse * _Nullable response, NSError * _Nullable error) {
__ handle response
}];
Request Construction
Manual
Both authenticated and anonymous resource calls starts from the ResourceRequest construction. The request object combines the following properties:
path- URI path, appended toResourceBaseURLset within theClientconfiguration.method- HTTP request method, can be one ofget,post,put,patch,headanddelete.parameters- a dictionary of parameters used for the request. Parameters are appended to the URL or provided within a body depending on the request method (respectivelygetorpost).parametersEncoding- the encoding used for params, possible values arejsonorformUrlThe default value isencodingJSON.body- a raw bady of the request. If specified it overwrites theparametersandparametersEncoding.multipartData- the object that represents the multipart data that should be sent. Themultipart/form-dataContent-Type header is added automatically. Only the HTTP POST method is supported for a multipart request. Note that if you add multipart data theparametersEncodingproperty is neglected.headers- additional headers added to the HTTP request. The Onegini SDK takes the responsibility of managing theAuthorizationandUser-Agentheaders. These cannot be modified / provided.
path can be set to an absolute URL and can vary from that one set in the model. The domain for a different base URL has to be protected with a valid certificate, otherwise the pinning mechanism will not allow the fetch to be executed.
In order to create an instance of the ResourceRequest you may use ResourceRequestFactory:
public static func makeResourceRequest(path: String,
method: HTTPMethod = .get,
parameters: [String: Any]? = nil,
body: Data? = nil,
headers: [String: String]? = nil,
parametersEncoding: ParametersEncoding = .JSON) -> ResourceRequest {}
public static func makeMultipartResourceRequest(path: String,
method: HTTPMethod,
parameters: [String: Any]?,
multipartData: [MultipartData]) -> ResourceRequest {}
- (instancetype)initWithPath:(NSString *)path method:(NSString *)method;
- (instancetype)initWithPath:(NSString *)path method:(NSString *)method parameters:(nullable NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *)parameters;
- (instancetype)initWithPath:(NSString *)path method:(NSString *)method parameters:(nullable NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *)parameters encoding:(ONGParametersEncoding)encoding;
- (instancetype)initWithPath:(NSString *)path method:(NSString *)method parameters:(nullable NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *)parameters encoding:(ONGParametersEncoding)encoding headers:(nullable NSDictionary<NSString *, NSString *> *)headers;
- (instancetype)initWithPath:(NSString *)path method:(NSString *)method body:(nullable NSData *)body headers:(nullable NSDictionary<NSString *, NSString *> *)headers;
- (instancetype)initWithPath:(NSString *)path method:(NSString *)method parameters:(nullable NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *)parameters multipartData:(NSArray<ONGMultipartData *> *)multipartData;
In addition to ResourceRequest, which is immutable by design there is a counterpart - MutableResourceRequest that allows you to modify all of the available properties one by one.
Example of request construction
let request = ONGResourceRequest(path:"_api_users_" method:"GET" parameters:{"username": "foo@bar.baz"})
__ mutable version
let request = ONGMutableRequest(path:@"_api_users_" method:"GET")
request.headers = {"X-Flags": "1000010"}
request.parameters = {"username": "foo@bar.baz"}
request.parametersEncoding = .JSON
ONGResourceRequest *request = [[ONGResourceRequest alloc] initWithPath:@"_api_users_" method:@"GET" parameters:@{@"username": @"foo@bar.baz"}];
__ mutable version
ONGMutableRequest *request = [[ONGMutableRequest alloc] initWithPath:@"_api_users_" method:@"GET"];
request.headers = @{@"X-Flags": @"1000010"};
request.parameters = @{@"username": @"foo@bar.baz"};
request.parametersEncoding = ONGParametersEncodingJSON;
Request Builder
In order to simplify request construction the SDK offers a ONGRequestBuilder class, that allow you to build new immutable requests through a set of methods
that reflect ONGResourceRequest properties and build an actual request instance by calling the -[ONGRequestBuilder build] method:
@interface ONGRequestBuilder : NSObject
- (instancetype)setMethod:(NSString *)method;
- (instancetype)setPath:(NSString *)path;
- (instancetype)setParameters:(NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *)parameters;
- (instancetype)setParametersEncoding:(ONGParametersEncoding)parametersEncoding;
- (instancetype)setBody:(NSData *)body;
- (instancetype)setMultipartData:(NSArray<ONGMultipartData *> *)multipartData;
- (instancetype)setHeaders:(NSDictionary<NSString *, NSString *> *)headers;
- (ONGResourceRequest *)build;
@end
Example request construction using the builder
let request = ONGRequestBuilder().setMethod("GET").setPath("_api_users").setParameters({"username": "foo@bar.baz"}).build()
ONGResourceRequest *request = [[[[ONGRequestBuilder builder] setMethod:@"GET"] setPath:@"_api_users"] build];
Handling the resource response
The responsibility for handling the fetched resource response belongs to the completion block passed into fetchResource:completion:. Below
you can find the explanation of the two possible outcomes for fetching resources.
Resource call completion
[client fetchResource:request completion:^(ONGResourceResponse * _Nullable response, NSError * _Nullable error) {
__ handle the response
}];
The completion block will be called whenever a fetch resource call is completed. The following values are provided:
response- the object containing the status code, headers and the bare data containing the body which needs to be decoded.error- defines the type of error that occurred. Depending on the error reason the following domains are possible:ONGFetchResourceErrorDomain(only for authenticated resource requests),ONGFetchAnonymousResourceErrorDomain(only for anonymous requests),ONGFetchUnauthenticatedResourceDomain(only for unauthenticated resource requests), theONGGenericErrorDomainin case of a generic error or theNSURLErrorin case of a http related error.
Example resource call implementation with a JSON encoded payload
client.fetchResource(request) { response, error in
if response?.statusCode < 400, let data = response?.data {
do {
let json = try NSJSONSerialization.JSONObjectWithData(data, options: [])
__ further response handling
} catch {
__ response is not JSON encoded
}
} else {
__ handle error
}
}
[client fetchResource:request completion:^(ONGResourceResponse * _Nullable response, NSError * _Nullable error) {
if (response && response.statusCode < 400 && response.data) {
NSDictionary *json = [NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:body options:0 error:nil];
__ further mapping of JSON
} else {
__ handle error
}
}];
Handling resource call errors
In case of a resource call failure the SDK will provide an error. Depending on the error reason and resource call type the following domains are possible:
ONGFetchResourceErrorDomain (only for authenticated requests), ONGFetchAnonymousResourceErrorDomain (only for anonymous requests), ONGGenericErrorDomain,
NSUrlError (in case of http related errors).
Example error handling
userClient.fetchResource(request) { response, error in
if let error = error {
switch error.code {
case ONGFetchResourceError.UserNotAuthenticated:
__ user isn't authenticated
case NSURLError.Cancelled:
__ cancelled explicitly, ignore
break
default:
__ default error handling
}
} else {
__ regular response handling
}
}
[userClient fetchResource:request completion:^(ONGResourceResponse * _Nullable response, NSError * _Nullable error) {
if (error) {
switch(error.code) {
case ONGFetchResourceErrorUserNotAuthenticated:
__ user isn't authenticated
break;
case NSURLErrorCancelled:
__ cancelled explicitly, ignore
break;
default:
__ default error handling
break;
} else {
__ regular response handling
}
}
}];
Running resource call handling
Both authenticated and anonymous resource calls return an instance of the ONGNetworkTask. This object allows you to control and observe the execution by
inspecting various properties:
state- enumONGNetworkTaskState, describing whether task is running, suspended, cancelled or completed.identifier- unique task identifier.request- request with which the resource call has been made.response- instance ofONGResourceResponse. This value fulfilled upon request completion and contains useful information likeHTTP Status Code, response headers and the actual body of the response. For advanced usage it provides a reference to theNSHTTPURLResponseobject.error- instance ofNSErrorfulfilled in case of a request failure. It might be of theNSURLErrorDomainorONGGenericErrorDomain.
You can control tasks through the following methods:
cancel- cancel a running or suspended task.suspend- suspend a running task.resume- resume a suspended task.

